In recent years, there has been a growing emphasis on healthy eating and incorporating nutrient-rich foods into our diets. One such nutrient that often goes unnoticed is cellulose.
Cellulose is a complex carbohydrate found in plant cell walls, and while it is indigestible by humans, it offers many benefits for our overall health and well-being.
This blog post will delve into the top 10 cellulose benefits that make you want to add it to your diet. So, let's explore the wonders of cellulose and its positive impact on our bodies.
Related Article: 7-Day Bodybuilding Diet Plan to Build Muscle and Lose Fat
What Is Cellulose and Its Types?

Cellulose is an essential component of plant cells that protects them from damage, but it does have an integral role in the human body. Since it is a part of plant cells, it's entirely organic, safe, and not digestible by the human body, yet has a vital role.
Cellulose is an insoluble fiber, and it remains unbroken in the body. It is required to ease certain medical conditions such as constipation or diverticulitis. Apart from treating such conditions, insoluble fibers constitute a significant part of the diet and should be eaten regularly.

There are two types of fibers:
- Soluble fiber
- Insoluble fiber
Soluble fiber is dissolved easily, whereas insoluble fiber does not break down. Eating more fiber can help you in a variety of ways. According to American Heart Association diet recommendations, taking at least 25 to 30 grams of fiber is recommended.
Eating fiber-rich food can benefit your body in several ways. High-fiber diets have a significant role in decreasing diseases such as cardiovascular issuess, easing digestion, managing cholesterol, and keeping blood sugar in check.
Related Article: Scientists Say Digestive Enzymes Are Key to Fighting Obesity
Nutritional Value of Cellulose
Cellulose does not have any nutritional component nor provide energy to the body. It does not contain any nutrients essential for maintaining good health. Cellulose only has insoluble fiber, which remains unchanged in the body.
It is an ideal choice to consume a lot of fiber in your diet, but it has to be combined with other food sources so that your body receives all sorts of nutrients. Ensure that you do not entirely rely on cellulose to fight the risk of diseases and infections, and include diverse food items in your daily meals.
Benefits of Cellulose
Insoluble fiber promises to provide maximum benefits to the body. That is why it is strongly recommended to have enough insoluble fiber and not to cut it down if you want to avail of all its benefits.
"Let food be thy medicine, and let cellulose be the foundation of a nourishing and healthy diet."
- Hippocrates (Father of Medicine)
Following are explained some of the positive benefits of cellulose:
1. Produces Healthy Bacteria
Intestinal microflora might help in dealing with significant health conditions. These bacterial species have important roles, such as synthesizing amino acids and vitamins and helping in the effective caloric distribution in the body. Healthy gut bacteria help to overcome multiple diseases and ensure the quality of life.
A continuous increase in fiber has improved gut bacteria, helping primary body functions. Fiber helps increase the number of bacteria needed for the breakdown of fiber and provides short-chain fatty acids to the body. Eating fiber helps your body to develop good and healthy bacteria.
2. Smooth Bowel Movements
Many often experience disturbed bowel movements due to digestion issues or underlying problems. The disturbed bowel movements can cause difficulty in excreting and induce an uncomfortable feeling. According to research, it is proven that fiber has a positive impact on improving bowel movements.
The fiber in the diet will help absorb more water, which will work to improve the excretion process. People experiencing severe constipation can also benefit from dietary fiber as it binds more water to the excretory materials and helps soften the stools.
3. Helps Manage Weight

Many people need to add more fiber to their diet. This preliminary fiber consumption increases weight, resulting in obesity, which is further linked to many health conditions. Fiber intake has an inverse relation with body fat composition. The more fiber you have in your diet, the less of a chance you have of becoming obese. So, it is essential to incorporate fiber-rich foods in your diet to manage your weight effectively and have a healthy lifestyle.
You should also try the Fat Burner supplements by DMoose, which suppress the appetite, boosts your energy, and enhances your overall performance with weight management.
4. Decreases Risk of Metabolic Disorders
Metabolic disorders result from altered body metabolism, which fails to provide necessary nutrients. Many diseases can fall into metabolic disorders, such as blood glucose levels, hypertension, etc. Fiber intake has helped much in reducing the symptoms of metabolic syndrome.
High-fiber diets have a positive role in managing metabolism and dealing with metabolic diseases. A study was conducted to assess the role of dietary fiber on metabolic disorders. The results showed that a fiber-rich diet has a positive link with reducing the severity and decreasing the symptoms of metabolic disorders.
5. Helps Manage Blood Glucose
An experiment conducted on six individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus showed that consuming a fiber-rich diet can help manage blood glucose. The result revealed that a high-fiber diet is inverse to blood glucose management and can help reduce diabetes-induced disease. Fiber can also improve the glycemic control of diabetic patients with the help of fiber diets. Fiber is found in many vegetables and fruits. People with diabetes must choose healthy food with a low glycemic index to lower blood sugar.
6. Decreases Cholesterol Levels
Hyperlipidemia is a condition in which a person experiences severe high cholesterol levels. A fibrous diet can help in decreasing cholesterol levels and improve heart health. Liver cholesterol accumulation is also reduced with the help of dietary fiber.
The research has studied an inverse relation between fiber consumption and cholesterol levels. Adding enough fiber to the diet will also help control the risk of heart disease. Consuming enough fiber is the best choice to manage your cholesterol levels, as it helps absorb bile salts and control cholesterol accumulation.
7. Protective Role in Cancer
Cancer is the uncontrolled cell production in the body. People with a slightly malfunctioning digestive tract can face severe conditions like colorectal cancer. Fiber intake has shown a protective role against cancer and its symptoms, as proved by various research.
Insoluble fiber has a protective role against various forms of cancers. The fiber components effectively bind with the carcinogens, help eliminate this toxic substance, and help reduce the incidence of various forms of cancers.
8. Helps Treat Diverticulitis
The formation of small and bulging pouches in the intestine, which then gets inflamed, is known as diverticulitis. The condition can be painful often and should be treated with relevant techniques. A high-fiber diet has shown a positive association with reducing the symptoms of diverticulitis.
The role of fiber in reducing the symptoms of diverticulitis has also been supported by research. The condition is quite common in men and can be treated with enough care and by adding more fibrous foods to the diet. It is necessary to have insoluble fiber in the diet to counter the effects of diverticulitis.
9. Suppresses Appetite

The fiber in the diet helps control appetite and suppress it in some cases. Fiber binds with water and forms a gel that creates a feeling of fullness and thus contributes to decreased food intake. That is why it is important to consume fiber to deal with the symptoms of obesity.
Many healthy foods are available, which also provide fiber to the body. Apart from that, you can also take fiber supplements to control or decrease appetite. The technique is beneficial for people with class one or two obesity.
10. Promises Life Longevity
A fibrous diet helps reduce the severity of various diseases, so it has become evident that consuming fiber can help increase longevity. It is seen that people with more fiber in their diet have helped increase their lifespan.
Fiber helps deal with heart diseases which are a significant cause of death. That is why it is advised to have enough fiber in the diet to live in good health.
How Much Do You Need Cellulose?

Fiber should have a major part in your daily meals. The fiber consumption requirements vary with each person. The following section explains some primary food sources and the amount that you should consume:
Food Containing Cellulose
Foods are a significant source of insoluble fiber. Consuming them can help in controlling various diseases. Some of the common food choices which have sufficient cellulose are:
- Flaxseeds
- Kidney beans
- Fruits and vegetables such as broccoli, avocados, and potatoes.
- Whole wheat products
- Bran cereals
- Celery
- Nuts and beans
- Raisins
Supplements

Food choices are a good source of insoluble fiber, but supplements are the best choice if you want to give an instant boost to your fiber intake. The probiotic supplement by Dmoose is the best choice to consume. The supplement helps in improving digestive function and also helps in the easy digestion of nutrients.
The probiotic supplement has also shown an improved immune system in people. The supplement will also help you achieve the recommended amount of fiber and fight various diseases.
Make Sure You Get Enough
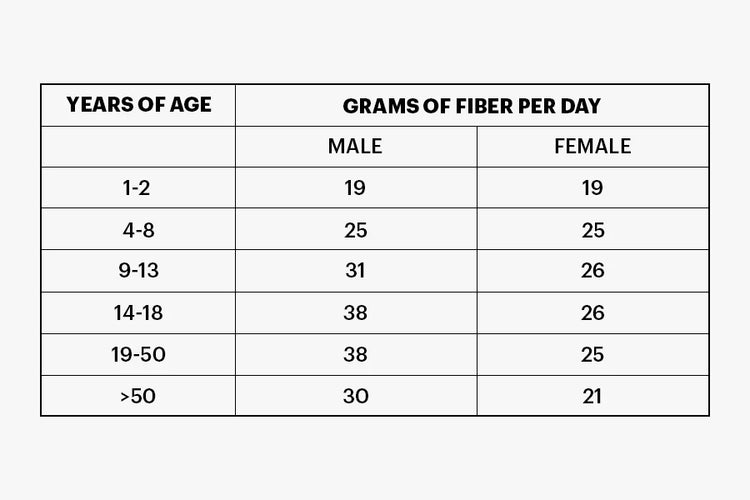
Consuming enough fiber will not cause any negative impact on health. Your meal plan should constitute high-fibrous foods so you can have your daily dose of fiber. The recommended amount of fiber is shown below.
Conclusion
Cellulose might remain indigestible in the body, but it does promise to bring numerous benefits to health. Consuming cellulose-rich foods can defend against heart, digestive tract diseases, etc. Cellulose has no adverse effects on the body so one can have it easily.Health professionals added fiber as an essential part of food and diet. Add fiber-rich foods to the diet or take help from supplements if needed.
Reading List
Article Sources
- Quigley, Eamonn M. M. "Gut Bacteria in Health and Disease." Gastroenterology & Hepatology, vol. 9, no. 9, Sept. 2013, pp. 560-69.
- Myhrstad, Mari C. W., et al. "ietary Fiber, Gut Microbiota, and Metabolic Regulation-Current Status in Human Randomized Trials." Nutrients, vol. 12, no. 3, Mar. 2020, p. 859. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12030859.
- Nakao, Makoto, et al. "sefulness of Soluble Dietary Fiber for the Treatment of Diarrhea during Enteral Nutrition in Elderly Patients." Nutrition, vol. 18, no. 1, Jan. 2002, pp. 35-39. ScienceDirect, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0899-9007(01)00715-8.
- Slavin, Joanne L. "ietary Fiber and Body Weight." Nutrition, vol. 21, no. 3, Mar. 2005, pp. 411-18. ScienceDirect, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2004.08.018.
- Chen, Jia-Ping, et al. "ietary Fiber and Metabolic Syndrome: A Meta-Analysis and Review of Related Mechanisms." Nutrients, vol. 10, no. 1, Dec. 2017, p. 24. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10010024.
- Oda, Taishi, et al. "ffects of Soluble and Insoluble Fiber Preparations Isolated from Oat, Barley, and Wheat on Liver Cholesterol Accumulation in Cholesterol-Fed Rats." Journal of Nutritional Science and Vitaminology, vol. 39, no. 1, 1993, pp. 73-79. J-Stage, https://doi.org/10.3177/jnsv.39.73.
- Wu, Yihua, et al. "ssociation between Dietary Fiber Intake and Risk of Coronary Heart Disease: A Meta-Analysis." Clinical Nutrition, vol. 34, no. 4, Aug. 2015, pp. 603-11. ScienceDirect, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2014.05.009.
- Papandreou, Dimitrios, et al. "he Role of Soluble, Insoluble Fibers and Their Bioactive Compounds in Cancer: A Mini Review." Food and Nutrition Sciences, vol. 06, no. 01, Jan. 2015, p. 1. www.scirp.org, https://doi.org/10.4236/fns.2015.61001.
- Aldoori, Walid H., et al. " Prospective Study of Dietary Fiber Types and Symptomatic Diverticular Disease in Men." The Journal of Nutrition, vol. 128, no. 4, Oct. 1998, pp. 714-19. Silverchair,https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/128.4.714.
- Ma, Wenjie, et al. "ntake of Dietary Fiber, Fruits, and Vegetables, and Risk of Diverticulitis." The American Journal of Gastroenterology, vol. 114, no. 9, Sept. 2019, pp. 1531-38. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.14309/ajg.0000000000000363
- "a href="https://www.pcrm.org/news/health-nutrition/high-fiber-diets-increase-lifespan">High-Fiber Diets Increase Lifespan." Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine, https://www.pcrm.org/news/health-nutrition/high-fiber-diets-increase-lifespan











