Nutrition has a major role in bringing positive results to the body. For athletes, nutrition significantly contributes to their training sessions and makes them more productive and effective. A right meal plan with adjusted portions of all macronutrients will work for athletes and derive better results.
Exercising and meals go hand in hand. It is a universal concept that eating the right nutrients affects athletes' performance capability and helps them grow muscles. Not only that, but the right meal plan also helps in reducing the post-exercise damage, eliminating chances of injury, and boosts performance during competitions.
The nutritional needs of athletes are generally larger than the normal population, and these needs vary among athletes. Some would need a larger portion of meals with more calories, while others can work on fewer calories.
Athletes have to pay attention to their meal timings, the type of food they are having, and the number of nutrients they are consuming in one go. These factors determine their strength and performance capabilities and train them to perform better during competitions.
The hydration status of athletes also needs to be monitored throughout the day. The food consumption needs of athletes are determined by the type of sport and the intensity of exercise they perform. The food choices of athletes before competition dates can bring huge and significant changes to their performance.
Athletes are involved in extensive and intense training sessions, which require more energy and enhanced consumption of nutrients. The training experts have provided nutritional guidelines to athletes, which can help them optimize their performance and gain more muscle mass.
Professional athletes consume a sufficient amount of energy, including all major food groups, and in certain situations, they also rely on supplements for meeting RDAs of vitamins and minerals.
Nutrient Distribution for Athletes

It is essential to follow a correct and balanced distribution of nutrients with an active exercise routine throughout the day. The athletic nutrients distribution majorly covers integral food options. Athletes need to add healthy food choices to keep their bodies working at an optimal and balanced rate.
The following are the guidelines for athletes according to the 2003 International Olympic Committee (IOC) Consensus Conference on Nutrition in Sport:
Calories
The caloric needs of athletes depend on their intensity, the timing of exercises, age, and body composition. The type of training is a major factor that determines the caloric needs of athletes. The intensity of exercise is also considered while planning the caloric consumption of athletes.
In many cases, athletes have to consume more calories to maintain or gain weight. If the target is to reduce some weight, the best approach would be to reduce some calories.
By estimating the basal metabolic rate and calculating it with physical activity level, you can estimate calories that you will need for intensive workout sessions. Basal metabolic rate is the number of calories that are burnt during rest.
Calorie requirements: BMR*Physical activity level
Carbohydrates

Carbohydrates are essential macronutrient that provides fuel to the body for proper functioning. The carbohydrates needed are generally higher in athletes due to their training sessions. After calculating the calories needs of athletes, the next step would be to analyze the number of carbohydrates.
The guidelines for carbohydrate consumption in athletes are 2.3-3.2 g/lb./day during periods of low-intensity workouts. However, the recommended carbohydrates are 3.2-4.5 grams per lb. per day for longer and higher intensity workout sessions. The type of exercise and its timing are integral factors in determining carbohydrate distribution.
Research has shown that athletes often fail to consume the recommended amount of carbohydrates. The distribution of body weight and fat deposition are some reasons for the low consumption of carbohydrates. Choosing the right carbohydrate choices will maintain adequate glucose levels and help in the recovery periods as well.
Proteins
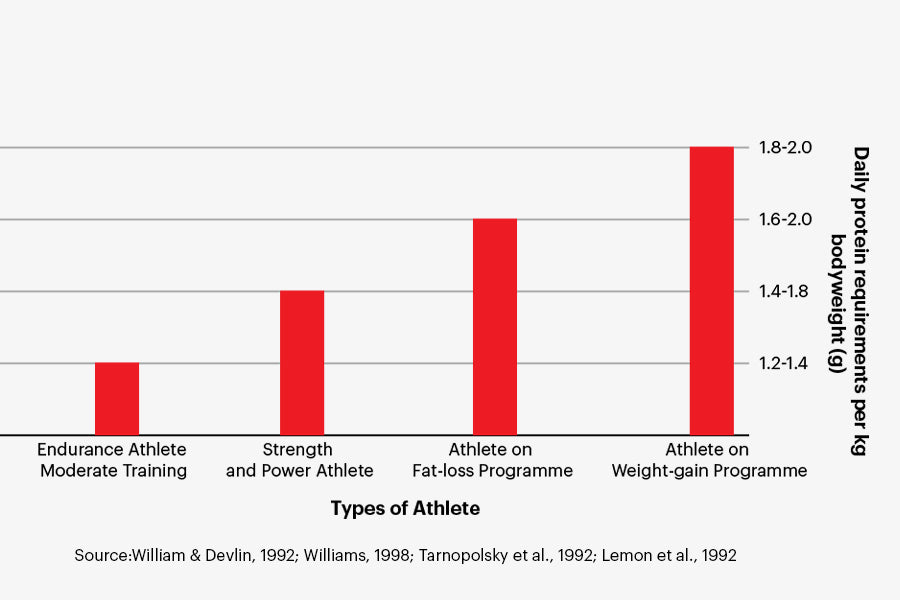
Proteins have essential amino acids in them, which help in repairing the muscles and damage post-exercise. The protein requirements of athletes are slightly greater than normal people. It is because athletes need to recover the breakdown of muscles and add more muscle mass.
The protein requirement for athletes varies from 0.75 to 1.6 grams per pound bodyweight each day. On the other hand, a normal person would need only 0.36 grams of protein per pound. Athletes consume more proteins because they need to maintain their weight and add more fibers to their muscles.
The intense training of athletes causes the extreme breakdown of muscles. The excess or much larger portion of protein plays a key role in recovery and maintaining optimal performance levels. Consuming a meal of protein and carbohydrates after exercise helps in speeding up muscle recovery.
Fats

Fats are important micronutrients that are an important component of cell membranes and serve as a cushion to the organs. They are a rich source of many essential fatty acids such as omega 3, fat-soluble vitamins that aid in the healing and recovery of the muscles.
The recommended amount of fats for athletes is 25% to 30% of calories. It is better to have 25% calories from fats for normal functioning. The type of fat that is consumed should be monitored. It is advisable to add more healthy fats to the diet and include little or no saturated fat.
The unsaturated fatty acids help in many processes and improve performance, and aid in recovery. Omega 3 fatty acids are healthy for the body and work in many important processes.
Related Article: Everyone Talks About Pre-Workout Supplements But Is It Bad For You?
Hydration
Athletes should pay much attention to their hydration status to avoid dehydration. Consuming less water can have an impact on the performance of athletes. Dehydration can also become a reason for several heat-related illnesses in athletes as they have to train for longer periods and in uncertain weather.
Athletes should monitor their water consumption before training sessions to avoid any uncomfortable feelings. The guidelines of hydration status suggest having maximum fluids to overcome the water loss during exercises.
Athletes can also consume sports drinks as a substitute for water as they help them retain water and provide all essential electrolytes.
Vitamins and Minerals
If an athlete has a restricted diet, then supplements for vitamins and minerals become necessary. They need to have adequate levels of all vitamins and important minerals so that supplements can prevent the risk of diseases.
A balanced diet ideally provides all essential vitamins and minerals to athletes. However, in cases such as the female athlete triad, the need for vitamins and minerals is generally increased and should be met. Each vitamin has its role in the body and must be consumed according to the set RDAs'.
Many athletes do not consume a balanced amount of vitamins and minerals from their diet, and hence they need to add supplements.
Distribution of Meals in Athletes
Carbohydrates, proteins, and fats are the major food sources that provide fuel and energy to the body. It is essential to pay attention to the timing of the meal and adjust the quantity accordingly.
The most critical meal timings in an athlete's life are before a training session, between the sessions, and having a post-workout meal with other meals depending on convenience.
Pre-workout Meals

Pre-workout meals play an important role in the performance capability of the athlete. Athletes should adjust the timing of consuming food before exercise for better performance.
In the same way, the type of food also has much significance here. Eating a carbohydrate-rich meal 2 to 3 hours before a workout fuels the body and delays fatigue.
Grabbing a pre-workout supplement here will help athletes get the right nutrients in the body, which are essential for endurance and strength in athletes. It is necessary to have a pre-workout meal to achieve maximum results from exercise sessions and more endurance.
During Exercise Meals

During exercise, meals are not important unless an athlete is exercising for more than 60 minutes. In such prolonged periods of exercising, having a quick meal is important for fueling energy sources. The best option would be to have an intra workout supplement or some carbohydrate-rich food that is easily digestible.
Having such supplements and meals will help athletes exercise better and delay the onset of fatigue. Consuming a drink or meal during exercise will also help in post-exercise recovery. Most importantly, it will allow you to exercise for a longer time without feeling tired or dizzy.
Post-workout Meals

It is the best practice to eat as early as possible after exercise ends. The body stores glycogen at a faster rate right after exercise ends. Eating post-workout is essential as it allows you to work at a better rate and fast rate. A post-workout supplement with all essential nutrients or a carbohydrate and protein meal will help to store more glycogen.
The post-workout routine emphasizes much on following good routines. Athletes should ensure that they are getting the right nutrients to prepare well for their next workout session.
How to Plan Your Workout Meal?

Whether you participate in regular physical exercises or not, you need to follow a well-planned and balanced meal to get the right nutrients. However, if you perform even a little physical activity, following the right eating routine becomes mandatory.
You need to calculate your total caloric needs and then adjust the carbohydrate, protein, and fat intake according to your body type and physical activity level. Make sure to add healthy food choices to your meal plan to make the most out of your workout sessions.
Related Article: Top 10 Cellulose Benefits That Will Make You Add it to Your Diet
A Meal Plan Designed for Better Results
The following meal plan is designed by experts that cater to almost everyone.
Meal plan
A glass of water before breakfast.
Breakfast
(At 10:00 a.m.)
- Two boiled eggs
- ½ cup orange juice
- One cup quinoa, cooked in water. With ½ medium banana, one and a half date, half cup strawberries, and six almonds.
(1 glass of water)
One Hour After Breakfast
(At 11:00 a.m.)
- 1 cup low-fat milk
(After 30 minutes, a glass of water)
Snack 1
(At 1:00 p.m.)
- ½ cup kidney beans, with 3 oz. of baked potato with skin and 1 cup of raw vegetables. (Onions, tomatoes, carrots, capsicum, cabbage, etc.)
(A glass of water)
Lunch
(A glass of water)
(At 2:00 p.m.)
- One-half apple and 1 cup strawberries in 1 cup of Greek Yogurt with 1 tbsp. Of grounded sunflower seeds.
(At 4:00 p.m.),
- 2 Tbsp. of Avocado
(A glass of water)
Training Time
5:00 p.m.
During Exercise
(At 5:30 p.m.)
- 1 cup of smoothie with one ¼ cup of watermelon, half cup water, a pinch of salt, a few lemon drops
- One whole wheat muffin
(500 ml of water, with half teaspoon salt and half teaspoon honey)
After Exercise
(At 6:20 p.m.)
- One cup fat-free dark chocolate milk with 1 tbsp. of pumpkin seeds.
- ½ cup mashed potato
(At 7:00 p.m.)
- ½ cup juice of cucumber and mint ( with lemon)
Snack 2
- 1/3 cup of cooked brown pasta, with 1 oz. of boiled chicken with skin and half cup vegetable ( cooked capsicum, carrots, cabbages)
(A glass of water)
Dinner
- 1/3 cup cooked rice, with ½ cup of cooked peas and 1 oz. of beef steak grilled with 1 tsp of olive oil and ½ cup boiled spinach.
(A glass of water)
The total number of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins in the above meal plan are listed below:
Total Calories: 2015 Kcal
Total Carbohydrates: 261 g
Total Protein: 71 g
Total Fat: 74 g
Tips and Considerations Related to Diet During Exercise Sessions
- Always add the right food choices to your diet that are full-filling and provide all essential nutrients.
- Closely monitor the timings of the meals for your convenience.
- Include light and digestible food options during exercises.
- Do not fear to try a supplement if needed.
- Pay attention to your hydration status to avoid any health condition.
- Add fiber and antioxidant-rich foods to the diet, such as strawberries.
- If you plan to increase weight, add nutrient-dense options to your diet.
- Adjust your food needs according to the type of exercise.
Conclusion
Athletes need an optimal supply of nutrients and energy for their proper functioning and improved performance during their competition days. They should monitor their hydration status adequately and pay sufficient attention to the food they consume by strictly following the meals’ timings.
Even if a normal person is engaged in some physical activity, it is important to follow a balanced meal plan. The caloric needs of such people and athletes are higher than those who have a sedentary lifestyle, and so they should check it regularly.
Article Sources
- Cotugna, Nancy, et al. “Sports Nutrition for Young Athletes.” The Journal of School Nursing, vol. 21, no. 6, Dec. 2005, pp. 323–28. SAGE Journals, https://doi.org/10.1177/10598405050210060401.
- Nutrition and Athletic Performance: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia. https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/002458.htm.
- Burke, L. M., et al. “Guidelines for Daily Carbohydrate Intake: Do Athletes Achieve Them?” Sports Medicine (Auckland, N.Z.), vol. 31, no. 4, 2001, pp. 267–99. PubMed, https://doi.org/10.2165/00007256-200131040-00003.
- Nazem, Taraneh Gharib, and Kathryn E. Ackerman. “The Female Athlete Triad.” Sports Health, vol. 4, no. 4, July 2012, pp. 302–11. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.1177/1941738112439685.
- Anita Bean-The Complete Guide to Sports Nutrition (Complete Guides) -A & c Black Publishers Ltd (2009) - Free Download PDF. https://kupdf.net/download/anita-bean-the-complete-guide-to-sports-nutrition-complete-guides-a-amp-c-black-publishers-ltd-2009_58fce38fdc0d60db62959e85_pdf.








